Blog post by Erin Kabba
LXD Research’s Empowering Educators: A Guide to Evaluating a Product Logic Model aims to assist educators in understanding and evaluating logic models created by companies to describe their products. The guide’s purpose is to empower educators, especially school leaders, to make well-informed decisions when choosing educational products that align with their goals and meet the requirements set by educational administrations.
What’s in the guide?
By the end of this guide, educators should be capable of discerning between high-quality and low-quality logic models and conducting critical assessments of educational products for their schools.
This guide includes knowledge on:
- The Purpose and Components of a Logic Model
- Identifying High-Quality Elements of a Logic Model
- Identifying Pitfalls and Warning Signs of Ineffective Logic Models
The Purpose and Components of a Logic Model
Logic models are essential in understanding educational products. A logic model is like a visual map that shows how different parts of a product connect – like resources, activities, and expected results. It provides a clear overview of what is needed for a product, what activities are happening, and what outcomes are expected. In contrast to research papers that provide a detailed understanding of the product, the logic model is a quick snapshot on a single page, providing educators with an overview and making the evaluation process efficient and accessible.
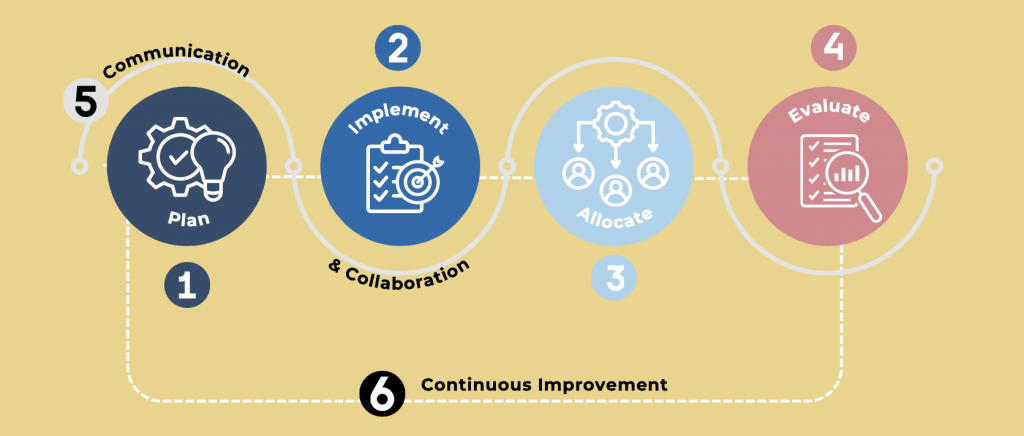
Logic models play crucial roles in education, such as aiding in strategic planning, guiding program design and implementation, allocating resources effectively, evaluating outcomes, facilitating communication and collaboration, and supporting continuous improvement. The key components of a logic model include problem statements, goals, resources, strategies and activities, outputs, and outcomes. Each element contributes to understanding and assessing the effectiveness of educational initiatives. This section provides an example logic model to illustrate how each component works.
Identifying High-Quality Elements of a Logic Model
There are some key elements to consider when using a logic model to evaluate the effectiveness of a program or product. A high-quality logic model has clear goals and outputs, highlighting the immediate effects of engaging with the product and research-based outcomes. This section explores the role of activities in achieving outcomes and highlights measurable outputs and distinct outcomes. Examples illustrate differences, and outcomes are categorized into short-term, intermediate, and long-term impacts, offering a comprehensive guide for assessing quality and effectiveness.
Identifying Pitfalls and Warning Signs of Ineffective Logic Models

Occasionally, logic models may fall short, hindering users from effectively determining the efficacy of educational products. This section highlights three main issues:
- unclear goals and problem statements,
- a lack of connection between logic model elements and
- the absence of clear outputs and outcomes.
Essentially, a logic model is like a story. Unclear goals make understanding a product’s purpose challenging, hindering communication and collaboration. A disconnection between logic model elements disrupts understanding of how a product works. Lastly, a lack of clear outputs and outcomes leaves the story incomplete, making it difficult to grasp the product’s impact.
Inside the guide, you will find guiding questions and a rubric for evaluating logic models, which will help you assess a program or product’s effectiveness.
Download a copy of Empowering Educators: A Guide to Evaluating a Product Logic Model and share it with your team!
