LXD Research’s Empowering Educators: A Guide to Evaluating a Product Logic Model can help EdTech product developers create logic models that meet the needs and expectations of educators. This guide aims to support educators in identifying high-quality logic models that educators, especially school leaders, can use to make informed decisions when selecting educational products that align with their goals and meet educational administration requirements.
What’s in the guide?
By reviewing this guide, product developers can create logic models that educators can easily discern between high-quality. When logic models clearly describe the key features of a product, they can help guide marketing and sales to differentiate the product in the market and clearly align the features to desired outcomes.
The guide includes knowledge on:
- The Purpose and Components of a Logic Model
- Identifying High-Quality Elements of a Logic Model
- Recognizing Pitfalls and Warning Signs of Ineffective Logic Models
The Purpose and Components of a Logic Model
Logic models are crucial in understanding and evaluating educational products. A logic model is a visual representation that maps out the connections between resources, activities, and expected outcomes of a product. It provides a concise overview, making the evaluation process efficient and accessible for educators.
Logic models play essential roles in education, such as aiding in strategic planning, guiding program design and implementation, allocating resources effectively, evaluating outcomes, facilitating communication and collaboration, and supporting continuous improvement. The key components of a logic model include problem statements, goals, resources, strategies and activities, outputs, and outcomes. Each element helps in understanding and assessing the effectiveness of educational initiatives. This section provides an example logic model to illustrate how each component works.
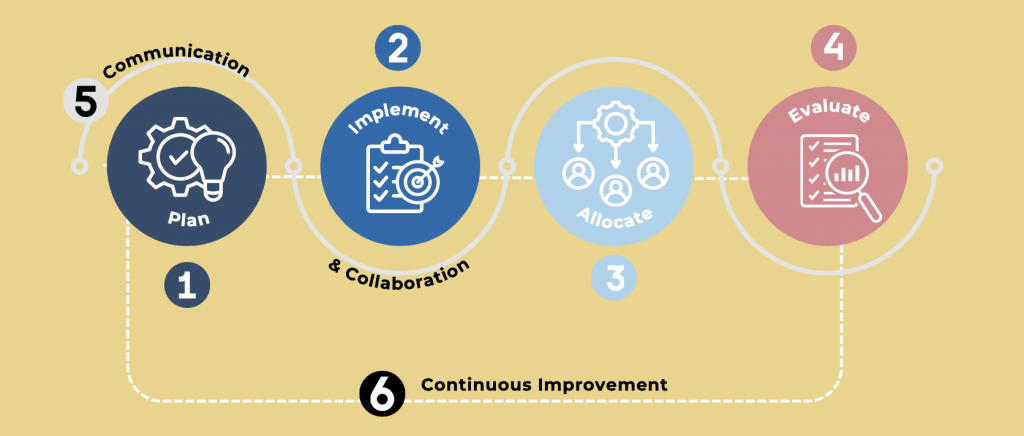
Identifying High-Quality Elements of a Logic Model
Key elements to consider when using a logic model to evaluate the effectiveness of a program or product are: A high-quality logic model has clear goals and outputs, highlighting the immediate effects of engaging with the product and research-based outcomes. This section explores the role of activities in achieving outcomes and highlights measurable outputs and distinct outcomes. Examples illustrate differences, and outcomes are categorized into short-term, intermediate, and long-term impacts, offering a comprehensive guide for assessing quality and effectiveness.
Recognizing Pitfalls and Warning Signs of Ineffective Logic Models

Occasionally, logic models may fall short, hindering users from effectively determining the efficacy of educational products. This section highlights three main issues:
- Absence of clear outputs and outcomes
- Unclear goals and problem statements
- Lack of connection between logic model elements
Essentially, a logic model is like a story. Unclear goals make understanding a product’s purpose challenging, hindering communication and collaboration. A disconnection between logic model elements disrupts understanding of how a product works. Lastly, a lack of clear outputs and outcomes leaves the story incomplete, making it difficult to grasp the product’s impact.
Inside the guide, you will find guiding questions and a rubric for evaluating logic models, which will help you assess a program or product’s effectiveness.
Download a copy of Empowering Educators: A Guide to Evaluating a Product Logic Model and share it with your team!